Q1. What is OTC process?
A. OTC stand for Order to Cash process. It represent entire sales process.
Steps involve in OTC cycle:
- Presales: Customer can inquire about product or request for quotation before placing order. Inquiry and Quotation can be generated in SAP to use as reference for sales document. Tcode: VA11- create inquiry VA21- Create Quotation
- Sales order creation– Sales document (sales order/contract) can be enter manually by sales or it can be created automatically via batch job. Tcode: VA01- create sales order, VA31 – create contract (VA02, VA32 – change & VA03, VA33- Display)
- Availability check: Once sales document is generated, availability check is use to decide if enough stock is available to fulfill customer needs
- Outbound Delivery: Delivery document hold record of delivery. Outbound delivery document is created with reference to Sales document. Once outbound delivery document is generated, Warehouse start picking and packing process. Tcode: VL01N – Create, VL02N – Change, VL03N- Display
- PGI (Post Good Issue): Once Goods packed and leave company warehouse, User can PGI outbound delivery document. PGI will move reduce stock from inventory with 601 movement type with reference to outbound delivery. Tcode: VL02N- change. Once PGI is done user will not allow make any change to delivery document.
- Invoice to Customer: After PGI, invoice can be generated manually or automatically using Batch job. Invoice will be sent to customer via email, printout mail or EDI
- Invoice settlement: Once customer initiate payment, it will clear AR account.
Q2. What is customer material info record?
A. Customer material info record link production material and Customer number to customer material number.
Customer material info record also hold information regarding delivery plant, Delivery priority, Item Usage.
During sales order creation, system read customer material info record and fetch customer material, Delivery Plant.
Sales document gives first priority to Customer material info record.
Q3. How storage location determine?
A. If storage location for picking is not specified in the order item, the system determines the storage location when it creates the outbound delivery and copies it into the delivery item. Otherwise, the storage location entered in the order item is used in the outbound delivery.
The system determines the picking location based on a rule defined in the delivery type. The following rules are shipped in the standard system:
MALA: The picking location is determined based on the shipping point, the delivering plant, and the storage condition for the material as defined in the material master.
RETA: Plant / Situation / Storage location
MARE: MALA then RETA
MSRE: Advance return inbound
Q4. Explain partner Determination configuration steps?
A. Steps to configure partner determination.
Define Partner Function: Partner function allow to define different type of partner.
For Example:
| Partner function |
Name |
Partner type |
| SP |
Sold – to – party |
KU |
| SH |
Ship – to – party |
KU |
| BP |
Bill – to – party |
KU |
| PY |
Payer |
KU |
Define partner determination procedure
- Click on partner determination procedure under control button
- Go to new entries
- Define your own partner determination procedure
- Save and Exit
Assign partner functions in the partner determination procedure
- Select our partner determination procedure
- Click on partner functions in procedure
- Go to new entries
- Specify partner functions like below
Partner determination procedure assignment
- Click on partner determination procedure under dialog structure
- Choose our account group from position button that we defined in OBD2
- Assign partner determination procedure that we created in the previous step
- Save and Exit
Account groups – Function assignment
- Click on account groups – function assignment button under dialog structure Go to new entries Specify partner functions
Partner determination procedure for sales document header
- SAP uses condition technique to determine partner functions for sales document header and item.
Q5. How plant determine?
A. Plant determination process has three steps in standard SAP:
- system checks customer-material info record, if plant is maintain plant data will be copy to sales document
- If Customer material info record is not maintain- system check customer master data to pull delivery plant information
- If no record found, system check material master data for delivery plant information.
Q6. What is difference between Sales order and Scheduling Agreement?
A. Sales Order: Request from a customer to a company to deliver a defined quantity of products or provide a service at a certain time. The sales area that accepts the inquiry is responsible for completing the agreement.
Scheduling Agreements: A customer scheduling agreement is an outline agreement with the customer containing delivery quantities and dates. These are then entered as schedule lines in a delivery schedule. Scheduling agreement contains either forecast or JIT delivery schedule.
Q7. What is difference between Scheduling Agreement (LZ) & Scheduling Agreement with Delivery order (LZM)?
A. In scheduling agreement, sales representative creates scheduling agreement and base on requirement from customer, populate delivery schedule for scheduling agreement. Scheduling agreement converted into outbound delivery. Sales representative decide delivery quantity base on release.
In scheduling agreement with delivery order, sales representative creates scheduling agreement (LZM), customer decide quantity needed. Base on that customer send EDI to create delivery order (types sales order) with reference to scheduling agreement. Sales representative creates delivery with reference to delivery order.
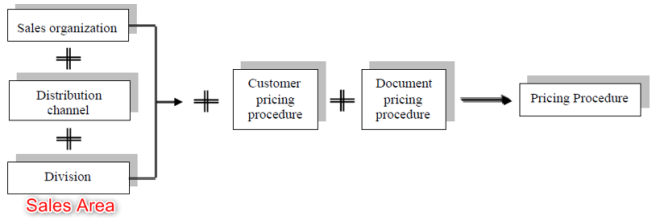
Q8. How pricing procedure determine?
A. SAP system check sales area, Customer pricing procedure (customer master) and Document pricing procedure (sales doc type). Base on this combination system determine pricing procedure.
Q9. Is it possible to create sales document without material?
A. No, it’s not possible to create Sales document without Material master record
Q10. What is copy control?
A. Copy Controls are short programs that are used when copying from one document to another. They consist of programs known as routines that inform the system how the data is to be copied from the source document to the target document.
The standard system already contains a number of these routines. However, it is possible to generate additional routines to fulfill business requirements not reached within the standard delivered system.
Copy controls are setup at three levels of the sales order; Header level, Item level and Schedule line level. The Schedule line level is only relevant when copying from sales order to sales order or from billing doc to sales order.
The Header Copy Routines are used to copy data from the Header of the Source document to the Header of the Target document. A number of copy routines are required; one for General Header data, one for Partner data, etc.
Tcodes:
- VTAA – control for copying from sales order to sales order
- VTLA – control for copying from sales order to delivery
- VTAF – control for copying from billing doc to sales order
- VTFA – control for copying from sales order to billing doc
- VTFL – control for copying from delivery to billing doc
- VTFF – control for copying from billing doc to billing doc
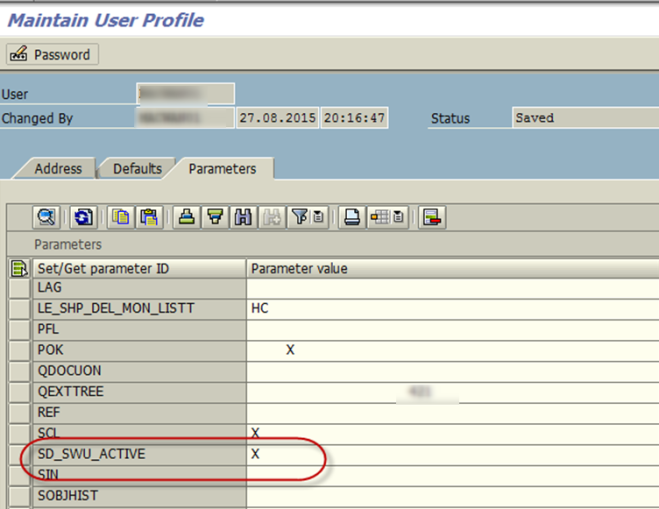
Q11. Is it possible to attach document on sales order?
A. Execute transaction SU3. Under Parameter enter parameter ID “SD_SWU_ACTIVE” and Parameter value X and click Save.
Attachment option will be available in sales document overview screen (ex: VA02, VA03)
Q12. Explain difference between Forecast and JIT?
A. Forecast delivery schedule provides the vendor with longer-term data regarding the quantities needed of a material and when delivery is required. In such schedules, the timing of delivery is usually expressed in terms of calendar months or weeks.
Just-in-Time (JIT) delivery schedule provides the vendor with data on required quantities and desired delivery dates/times covering the near future. In such schedules, the timing of delivery is usually expressed in terms of specific days or even times of the day.
Q13. Is it possible to update price on sales document?
A. To update price on sales document, go to VA02, click on item condition icon.
Click on Update button and select carry out new pricing option.
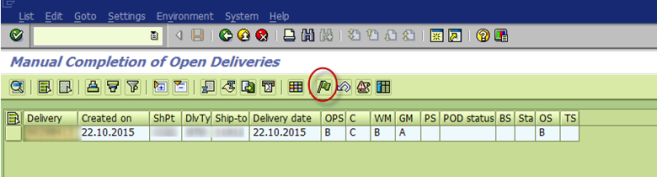
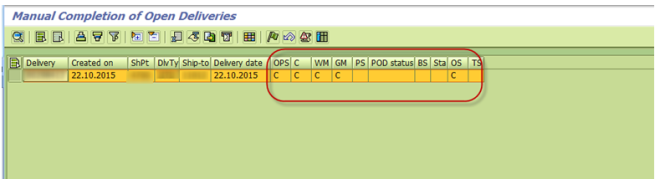
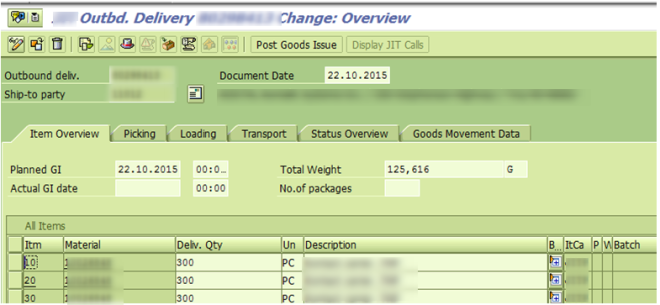
Q14. Explain outbound delivery?
A. Outbound Delivery: SAP document store information of good leaving plant location to fulfill customer requirement.
Tcode: VL01N – Create with reference/ without reference
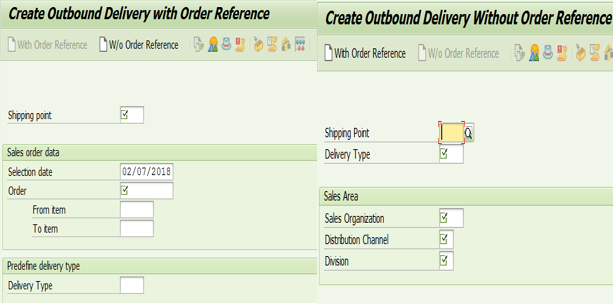
VL02N: Change outbound delivery information – to perform Post Goods Issues
VL03N: Display outbound delivery
Note: Delivery is document once it’s deleted it will not accessible on SAP server.
Q15. What is PGI? When can you PGI?
A. PGI Stand for Post Goods Issue.
When PGI is completed SD process integration with Inventory Management by reducing inventory stock qty. Material document reflect stock Quantity update.
And PGI also have integration with FICO by reducing stock value. Accounting document reflect stock value update.
Q16. What is incomplete log?
A. An incompletion procedure groups the fields together that must be checked for completion. If any of the fields are blank, the document is incomplete. Incompletion procedures can be assigned and maintained at various levels and for various document types:
- Sales header (different procedures can be assigned to different document types)
- Sales item (item categories can contain different procedures)
- Schedule line (each can contain different procedures)
- Partners (can maintain different procedures for each partner function)
- Sales activity
- Delivery header
- Delivery item
Configuration
- Set up Status Groups (OVA0).
- Define procedure (OVA2).
- Assign status group to fields (OVA2).
- Assign procedure to various document types as follows:
- Orders (VUA2)
- Deliveries (VUA4)
- Items (VUP2)
- Schedule Lines (VUE2)
- Partners (VUPA)
- Sales Activities (VUC2)
- Set Error or warning message (VUA2).
- Test expected results.
Q17. Explain difference between cash order and rush order?
A. Cash sales are a special sales document type “CS” that allow a business scenario where customer pays the money and picks the material immediately. System automatically generates delivery document type BV and it triggers output type RD03, which generates cash sales, order as output and can be given to the customer as billing. Cash sales order does not have any invoice. But system generates duelist for billing document type BV. In cash sales cash account directly updated.
Rush order (Doc type RO) is order when customer places the order and collects the items immediately or company ship the materials immediately. However, company only invoice the customer later. The system automatically creates a delivery when user save the sales order, but no invoice is printed. Instead, the system follows the standard procedures for creating the invoice.
Both the rush order and the cash sales process utilize the shipping conditions passed on from the sales document.
Q18. Explain third party sales order?
A. In third-party process the delivery of the goods required by the customer is not done by sales organization where customer orders. Instead, the request of the goods is forwarded to an external vendor who sends the material directly to the customer.
Third party step:
- Update Material Master sales view (Tcode; MM03) – Item category BANS
- Sales order (Tcode: VA01) is created for above material with TAS Item category.
- Purchase requisition is created automatically when sales order is saved. (view under environment – status overview)
- Purchase order (Tcode ME21N) is with reference to Purchase requisition (manually or automatically)
- Vendor procure goods and sends material directly to Customer.
- Vendor sends ASN for GR- company creates statistical Good receipt (T code VL31N/ MIGO) against Purchase order and Settle Vendor account (Tcode: MIRO Or ERS)
- Company also generate customer Invoice base on Order (Tcode: VF01)
Q19. Explain variant configuration?
A. VARIANT CONFIGURATION is a tool that offers the flexibility of the configuration of the material during the Sales order processing by the end user according to the customer requirements.
Variant configuration has integration with following applications:
CA = Classification
LO = Material master
PP = BOM and routings
PP – PI = Master receipts
SD = Sales, conditions
MM = Purchasing
CO = Costing
PP MRP production orders
Variant configuration offers a unique feature by which requirement of creating separate material for each variant of product is eliminated by using “configurable material”, that contains all the components and operations for production planning requirements.
Characteristics: Characteristics are used to define the features of configurable material. These characteristics are assigned to CLASS TYPE 300
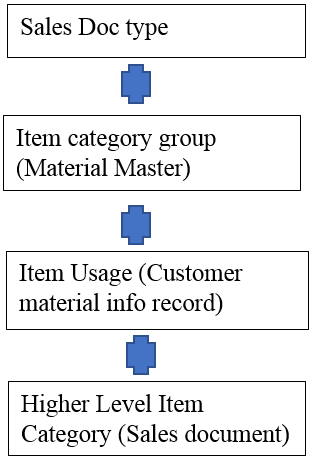
Q20. How item category determine?
Q21. Explain master data in SD module?
A. There are 4 important master data in SD module.
Customer master, Material Master (sales view) and Customer Material info record
Customer master:
The customer master record is the basis for all sales transactions as well as deliveries and payments. It maintains the details of the customer in the form of master data. Every customer master is made up with three (3) sections:
(A) General data [KNA1 – Table]
(B) Company code data [KNB1 – Table]
(C) Sales area data [KNVV – Table]
Important Transaction: XD01- Create (both Sales and Company code view), VD01 Create (Only sales view) and FD01 Create (only Company code view)
General data section: In general data section data about the customer’s personal details like name, address, and telephone numbers is maintained. The customer general data are company code, sales area independent.
Company code data section: It is only of interest to the accounting department. This data applies to only one company code. In company code data section data about the reconciliation account number, terms of payment, interest calculation indicator.
Sales area data section: In sales area data section data about the customer sales area like sales, shipping, billing related data are maintained.
Material Master:
Sales and Distribution responsible for Sales: Sale Org1, Sales Sale Org 2 and Sales: General / Plant view.
Sales Org1 View: Contain information regarding sales units, Delivery Plant, Minimum order Quantity and Tax data.
Sales Org2 View: Contain information regarding Material pricing group, Account assignment group, Item Category group (use to define item category on sales document),
Sales General/ Plant View: Contain information regarding availability check, loading group, transportation group (use for route determination)
Important Transaction: MM01 Create (For sales view- input Plant, Sales org and Division)
Customer Material Info Record:
Customer material info record link production material and Customer number to customer material number.
Customer material info record also hold information regarding delivery plant, Delivery priority, Item Usage.
During sales order creation, system read customer material info record and fetch customer material, Delivery Plant.
Important Transaction: VD51 Create, VD52 Change, VD53 Display
Q22. How pricing condition record are created?
A. To create condition record go to transaction VK11 choose condition type require new condition record.
Choose combination- (for example material customer combination). Item detail level specify pricing and validity date. Click save to generate condition record. To change or delete condition record got VK12 transaction.
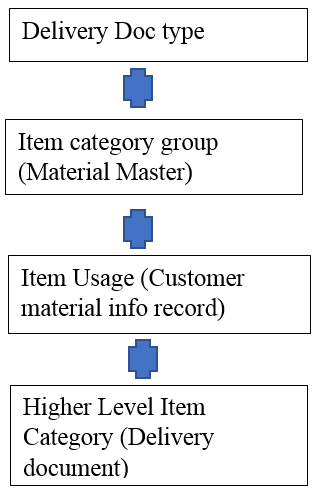
Q23. How delivery item category determine?
Q24. What is sales Group?
A. Sales group is constituent component in a distribution chain. Sales groups can be used for reporting purposes.
Employees can be assigned to a sales group. Sales group will assign to sales document. Sales group are responsible for sales area/Office
Q25. What are Enterprise Structure data for SD?
A. Setting up Enterprise Structure:
a. Sales Organization
b. Distribution Channel
c. Division
d. Sales Area
e. Common Distribution Channels
f. Common Divisions
g. Sales Office
h. Sales Group
i. Plants
j. Storage Locations
k. Shipping Points
l. Transportation Planning Point
m. Assigning Storage Locations to Plants
n. Assigning Sales Org / Distribution channels to Plants
Q26. Define control parameter for Rebate Process?
A. There are three control parameter for Rebate process.
- In definition of sales organization “Rebate” processing active should be check.
- In customer master (payer) “Rebate” should be active
- In billing document (F2) “Relevant for Rebate” should be activate.
Q27. How Schedule line determine?

Q28. What is difference between header and Item condition?
A. Header condition will be enter on header level of record. Header condition will be applicable to entire document. Header condition does not contain any access sequence and it’s manually enter in document.
Item condition record will be enter at item level. Each item can have their own item condition. Item condition will be applicable to only line where it enter. Item condition can contain access sequence. With access sequence item condition can be determine automatically.
Q29. How SAP SD is integrated with other SAP Module?
A. SAP SD is integrated to SAP Material Management (MM), SAP Production Planning (PP), SAP Finance (FI) and SAP Controlling (CO).
| Process |
Module |
| Availability Check |
MM |
| Credit Check |
FI |
| Costing |
CO |
| Tax Determination |
FI |
| Transfer of SD requirements |
MM and PP |
Q30. How route determine?
A. Route determination determine automatically base on following information.
Departure zone or country of the Delivering Plant
Destination zone or country of the Ship-to Party
Shipping condition from the Sold-to Party Customer master
Transportation group from Material Master