Q1. What is difference between purchase order and Scheduling agreement?
A. Purchase order is one time agreement with supplier to supply goods according to purchase order terms. Purchase order contain desire quantity, date, time and price.
For example: buying 1 laptop for $1000 dollar
Purchase order will be close once items is received.
Scheduling agreement is long term agreement with supplier to supply goods according to agreement terms. Scheduling agreement allow buyer and supplier to agree on term, total quantity and time period.
Scheduling agreements can be created either without reference to another document, or with reference to an outline agreement, an RFQ, or another scheduling agreement. Scheduling agreements can also create reference to centrally agreed contracts
Q2. What is PTP process?
A. PTP is procure to process step. It start with Purchase requisition process and end with Vendor invoice
Purchase requisition (ME51N) is create to capture procurement require internally
Purchase requisition review and approved by authorize people,
Approve purchase requisition will convert into purchase order (ME21N, ME59) and Purchase order will send out to supplier requesting good
Goods receipt done at plant level using MIGO and or Inbound delivery
Once good receipt is completed, invoice will be generate using MIRO transaction
Note: Scheduling agreement and or contract can be used instead of Purchase order
Q3. What is difference between contract and scheduling agreement?
A. Schedule agreement contains details of a delivery schedule but a contract just contains quantity and price information and no details of specific delivery dates.
Contract can be created with or without plant and can use as centrally agree contract to allow procurement for all plant belong that company code. Scheduling agreement can’t create without plant.
Scheduling agreement can be create with reference to contract but contract can’t be created with reference to scheduling agreement
Q4. What is different between Release order and Release documents?
A. When scheduling agreement or purchase order is created with reference to contract, scheduling agreement or purchase order is considered as release order.
Release documents – list of all scheduling agreements (purchasing documents) created with reference to contract. Release documents contain release information.
Q5. How to add Delivery schedule for schedule agreement?
A. Delivery schedule or release for supplier can be added manually or automatically.
If MRP is setup for material, system will automatically generate schedule lines for scheduling agreement.
To add or update schedule lines user needs to use ME38 transaction. From menu choose line and click on delivery schedule. User can add or modify schedule lines.
Remember if schedule lines are manually update, MRP run will not change those lines.
Q6. How to send release to supplier?
A. Release can be sent to supplier via email, print out or EDI. Delivery scheduler or release populated manually or automatically on scheduling agreement. Release output can trigger with job or manually using ME38 transaction.
To trigger output from SAP, consultant/administrator must setup configuration for output determination.
Q7. How to display status of message (email/Printout)?
A. To display status of printout – from contract/scheduling agreement overview -> click on message- on next screen will display overview of Message.
If status is green then message process without error.
If status is read then message does not process. User can view detail of error using processing log option.
Sq01 transaction can be used to view printout status.
SOST/SOSB transaction can be used to view email status.
Q8. How to reprint PO document without change?
A. Go to ME22N, select Message screen, and look for processed message (NEU) without change box checked.
Select line item and click on reprint.
To change printer select communication method option and change it desire printer. Further data option will allow you more processing option.
If you choose process immediately, Printout will trigger once you save document. If you choose send with own transaction, User needs to execute ME9F to trigger printout.
Q9. What is confirmation key what is use of confirmation control key?
A. Determine which confirmation category are expected for Purchasing document. Confirmation key is stored in Confirmation tab on Purchase order item detail.
For example confirmation category key – inbound delivery will allow user to create inbound delivery using VL31N transaction and trigger ASN.
Confirmation key rough GR will allow user to use only MIGO transaction (not VL31N) transaction
Q10. When user can use MIGO and VL31N transaction?
A. Confirmation control key on purchasing document (under confirmation tab on PO and additional data on scheduling agreement) allow user to use MIGO or VL31N transaction.
If confirmation key is selected as inbound user can use VL31N to create inbound delivery and generate ASN.
If confirmation key is selected as rough GR user can use MIGO transaction to create GR document.
Q11. How to display Material document?
A. User can use MB03 transaction to display Material document. Input Material doc number and year and click enter to display material document.
User can use MIGO transaction – from drop down choose display and material document. Enter Material document number and year click enter to display material document.
Q12. How to cancel Material document?
A. User can use MBST transaction to material document.
User input posting date, Material document, Material doc year and reason code and click enter.
Select line item you want to cancel and click Save to cancel.
MIGO Transaction can also use to cancel material document.
Q13. What is difference between good receipt and good issues?
A. Goods receipt (GR) is a goods movement with which the receipt of goods from a vendor or from production is posted. A goods receipt leads to an increase in warehouse stock.
Example: MB31 with movement type 101 to good receipt against Production order and MIGO with movement 101 to good receipt against Purchase order
Goods issue: A goods issue (GI) is a goods movement with which a material withdrawal or material issue, a material consumption, or a shipment of goods to a customer is posted. A goods issue leads to a reduction in warehouse stock.
Example: MB1A or MB11 with movement type 261 for good issues against Production order. VL02N- PGI with movement type 601 to reduce stock from inventory to customer
Q14. How to create invoice document?
A. User can use MIRO to create Vendor invoice manually.
With ERS system can initiate invoice settlement once Good receipt is posted.
Q15. What is ERS?
A. ERS — Evaluated Receipt Settlement is the process of settling goods receipt automatically. The Vendor Invoices are posted automatically (without actually receiving from the vendor) in the system based on the information in the purchase order and goods receipt. The settlement documents are sent automatically to the vendor in print, email or fax form
Prerequisites:
- In the vendor master data, the indicators for evaluated receipt settlement must be activated.
- A Confirmation is expected for the purchase order
- GR – IR Indicators and ERS Indicators should be activated in the PO
- Tax code must be maintained in the PO item
Q16. Explain different types of purchase documents?
A. Different types of PO:
- NB- Standard purchase order
- FO- Frame work Purchase order
- UB- Stock transfer order
Scheduling Agreement:
- LP: without release document
- LPA- with release document
Contract:
- MK- quantity contract
- WK – value contract
Q17. What is difference between subcontract and consignment?
A. Subcontracting process: When company or plant decide to outsource production operation to vendor. Subcontracting Process Company provide raw materials to supplier. Supplier use raw materials to manufacture finish product and return finish product to company.
Purchase info record is created with sub contract (L) item category.
Subcontracting purchaser order is created with subcontracting item category. Component tab will open to add raw materials on purchase order. Raw material are send to supplier using 541 movement types.
Vendor consignment: is process where Plant/company request a good from supplier and stock or goods remain at Vendor premises until goods consumed or moved to plant/company inventory. The supplier would not invoice until goods consume or moved from Vendor stock to inventory stock.
Vendor stock is handle as special procurement type in SAP.
Purchase info record is created with consignment item category. Rates and taxes information stored for pipeline and consignment info record.
Subcontracting purchaser order is created with consignment item category (K)
Settlement carried out with MRKO transaction.
Q18. Explain pipeline concept?
A.
Pipeline: Material flows through pipe from source to plant. For example Water, Oil etc.
There is no purchase order need for Pipeline material. Material consumption is recorded in SAP (Generally against cost element like cost center).
Purchase info record is created with Pipeline item category.
Settlement carried out with MRKO transaction.
Q19. What are different types of Physical inventory process?
There are two types of inventory process. Physical yearly inventory process and Cycle count inventory process.
Physical inventory process carried out on early basis mostly for warehouse storage location.
Cycle count inventory process carried out periodically, mostly for WIP (production) storage location.
Business decide how to conduct inventory process base on business needs.
Important Transaction code: MI01- Create, MI02 – Change inventory document, MI03: Display inventory process, MI21 – print Document, MI04- Enter count, MI05- Change Counted MI07 –Post, MI11- Recount
Material ABC analysis can be used for Cycle count:
MIBC- set cycle counting indicator
MICN- create physical inventory document.
Q20. Explain account determination process?
A.
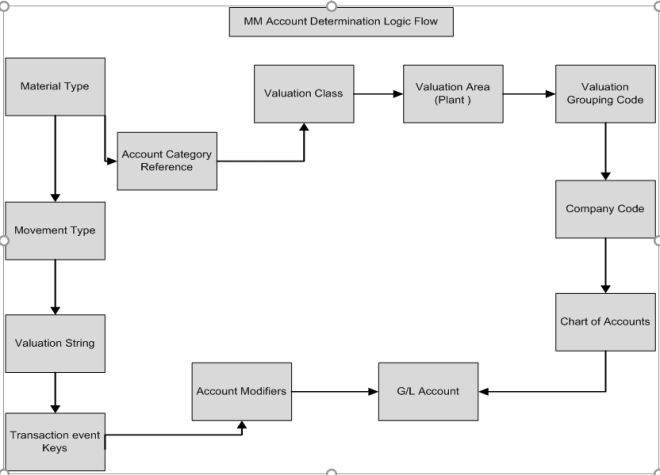
Q21. What is master data in MM?
A. There are five different types of master data.
Material Master: Hold information regarding materials.
Important view: Basic data1, 2 (Client independent) MRP1, 2, 3, 4 (plant and storage location dependent) Purchasing view (plant dependent), Storage data1 and 2 (storage location) Accounting 1 and 2 (plant dependent)
Important Transaction: MM01 Create, MM02 Change, MM03 Display, MM04 Display changes, MM06 Block, MM60- List of material, MMAM to Change material type
Vendor Master: hold information regarding Vendor. Vendor master consist of three view.
Basic view – basic information regarding vendor (address)
Company code view- Hold information regarding account, dunning, bank
Purchasing view: hold information regarding currency, payment terms, and partner function.
Important Transaction: MK01(purchasing) ,XK01 (Central- both finance and purchasing), FK01 Create (finance), XK02 Change, XK03 Display, XK04- Display changes, XK05 Block, XK06 Flag for deletion and XK07- Change account group
Purchase Info Record: Purchasing info record stores information on material and vendor supplying that material. For Example: Vendors current price of a particular material is stored in info record.
Purchase info record can be maintained at plant level or at purchasing organization level.
Purchase info record ca created manually or automatically. Purchase info record can be created for standard, subcontracting, pipeline and consignment item category.
Important Transaction: ME11 Create, ME12 Change, ME13 Display, ME14- Display changes, ME15- Flag for deletion
Source List: Source list include list of possible sources of supply for a material over a given framework of time. Source list specifies the time period of ordering of a particular material from a given vendor. Source list can be copied from one plant to another plant. Source list can be created atomically or manually
Important Transaction: ME01- Maintain, ME03 Display, ME04 Display changes ME07 – Delete
Quota Arrangement: Quota arrangement divides the total requirement of material among certain sources of supply i.e. vendors and then assigns quota to each source.
Important Transaction: MEQ1- Maintain, MEQ3 Display, MEQ4 Display changes MEQ7 – Delete
Q22. What Inventory management?
A. The inventory management comprises control of the stock transfers within the warehouse or intercompany distribution centers, display correct quality status and the accuracy of the physical inventory.
- Inventory management and physical inventory deals with
- Management of material stocks on a quantity and value basis
- Planning, Entry, and Documentation of all Goods Movements
- Carrying out the Physical Inventory
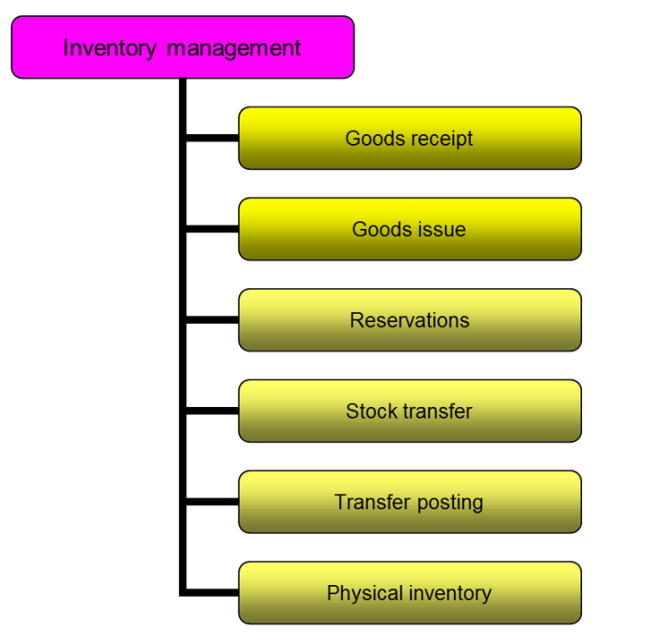
Q23. What is use of source list?
A. Source List: Source list include list of possible sources of supply for a material over a given framework of time. Source list specifies the time period of ordering of a particular material from a given vendor.
Source list can be used for MRP run, Base on source list setup, MRP can generate either purchase requisition or schedule lines
If source list is activated at material master, without source list it is not possible to generate schedule lines for scheduling agreement.
Q24. What is use of Purchase info record?
A. Purchase info record store pricing information for vendor- material combination. Purchase document like Purchase order and scheduling agreement reads purchase info record to pull price.
Minimum quantity on Purchase info record stop buyer to order less quantity on purchase order.
Q25. Explain release strategy?
A. Release strategy allow business to control procurement business spend by implementing approval process for each purchasing document.
Purchase requisition can release at item and header level.
All other purchasing documents can release at header level
Steps to setup Release strategies:
- Define Class: Tcode CL02. Characteristic will assign to class and Class will assign to release group to trigger release strategy
- Define Characteristic: Tcode CT04: Characteristic represent different condition like price range, plant, currency, org level, cost elements.
- Define release groups and assign them to class. User can use utilize overall release of purchase requisition option to apply release at same time.
- Define release codes and assign them to release groups.
- Define release indicators (e.g. 1-Blocked, 2-Released).
- Define a release strategy and assign release group and release code to a release strategy.
- Defining release statuses for the strategy (blocked and released) and Maintain classification
Q26. Name different types of stock and how to view them?
A. There are mainly three types of stock- Unrestricted, Quality and Block stock.
Unrestricted stock are free stock.
Quality stock are under quality check, cannot use for production.
Block stock are blocked due to poor quality, expired, rework. Block stock cannot use for production.
Special stock- Non valuated stock – Generally stock stored at company but belong to supplier or customer.
Q27. Explain pricing process in MM?
A. Pricing procedure is used during purchasing document creation. (For ex: PO, Scheduling agreement, Contract, RFQ). Pricing procedure consist of different pricing element like Material cost, discount, surcharge, tax, freight, etc. Pricing procedure is link to vendor and purchase department through the virtual schemas.
Step include in pricing procedure setup:
Define condition type: Tcode M/06: Condition type represent different types of charges. For example Material price, discount, freight etc. Condition types use the access sequence to find condition table to access condition record.
Define condition table: Tcode M/03: Condition table where system saves the all fields with the combination for individual condition record
Define Access Sequence: Tcode M/07: The main concept of Access sequence is, it searches condition record for condition type from condition table. One access sequence can contain one or multiple condition tables
Condition record: Transaction code MEK1- create: Condition record hold price for condition types.
Pricing Schema: Tcode M/08: Pricing schema contain different condition record that may need to define net price for material.
Pricing procedure determination: Schema group Purchase organization, Schema group Vendor will define pricing procedure.
Schema purchase group is assign to actual purchase org and schema group vendor is assign to vendor master (in purchasing view)
When user create any purchasing document (ex PO), system will check vendor master- purchasing view to fetch schema vendor group if any, then search schema purchasing organization associated for purchasing organization enter in purchasing document. Base on the information system will fetch associated pricing procedure.
Q28. Explain what is CBP? What is the difference between CBP and MRP?
A. CBP is the past consumption values of stock; it is used to forecast future requirements. On the basis of past consumption values, the net requirement of goods is calculated.
The difference between CBP and MRP is that when you plan materials using MRP, you have to predict the materials requirement based on sales and operations planning (SOP). While in CBP you have to predict the material requirement based on historical demand for materials.
Q29. What is difference between reference purchase org and Standard purchase org?
A. Purchase organization unit subdividing an enterprise according to the requirements of Purchasing. Standard purchase organization is company specific for one plant and it will default for that plant.
Reference purchase organization can be company code independent and allow to serve as reference other purchase organization to access condition, contract release orders on cross purchasing organization basis.
Q30. How invoice currency will determine? Is it possible to create invoice in different currency other than purchase order currency?
A. Invoice document read Purchasing document to fetch currency. Purchasing document reads main vendor master to fetch currency information.
It is possible to create invoice in different currency. User will allow to create invoice in different currency other than purchase order currency if user input currency manually before entering Purchase order data.
